Related:
-
Ideation: [tmp] aesthetic model research ideas
-
Experiment code: https://github.com/troph-team/trainlib/tree/main/projects/aesthetics/experiments/ex03_twidanhalf_regression
Experiment plan:
Prioritize:
-
Check data quality of the collected responses
-
Minimize error on reference dataset (the ones that were rated by 5 people)
-
See how model trained on the collected data generalizes on unseen data (eg. danbooru)
This over X:
-
… Haven’t thought of any good ones yet
Data process:
-
(only speculation, because I haven’t looked at the dump yet)
-
Currently, that’s all I plan to use, but maybe I will use something more in the future
| item | description |
|---|---|
| Remove voters with < 100 responses | Assuming no prior experience in voting, too little response could also mean unstable predictions |
| Remove data packs with <20% responses | Same reason as above |
| Apply Averaging | (for those with more than 1 rating: apply averaging) |
| Select samples with =5 responses | Some multi-rate samples don’t have enough response; only samples with 5 response will be used as reference, rest as training set maybe |
| (future): | |
| Maybe remove outliers using cleanlab | Will probably make the model behave more consistent, but it has tradeoffs |
Code references:
Data processing code:
-
not yet, but I plan to put data explorations processing here, to be separate from trainings:
-
troph-team/aeslib: aesthetics related notebooks; cleanup wip
Training code:
Feedback loop:
- Eagle plugin
(side project: distill novelai v4’s the aesthetic model):
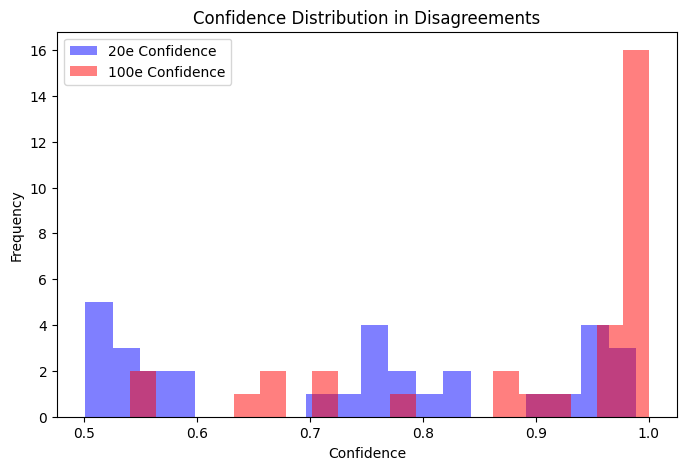
training over long period creates over-confidence:
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
df = res_all.copy()
# Identify disagreements
disagreements = df[df['label_20e'] != df['label_100e']]
# Plot confidence differences
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5))
plt.hist(disagreements['confidence_20e'], bins=20, alpha=0.5, label='20e Confidence', color='blue')
plt.hist(disagreements['confidence_100e'], bins=20, alpha=0.5, label='100e Confidence', color='red')
plt.xlabel("Confidence")
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
plt.title("Confidence Distribution in Disagreements")
plt.legend()
plt.show()- both models have similar accuracy, but 100e model has much higher confidence.
- distill-lab/distill-n4_00-01_combined_cls_v1b2 · Hugging Face
- distill-lab/distill-n4_00-01_combined_cls_v1b2-100e · Hugging Face
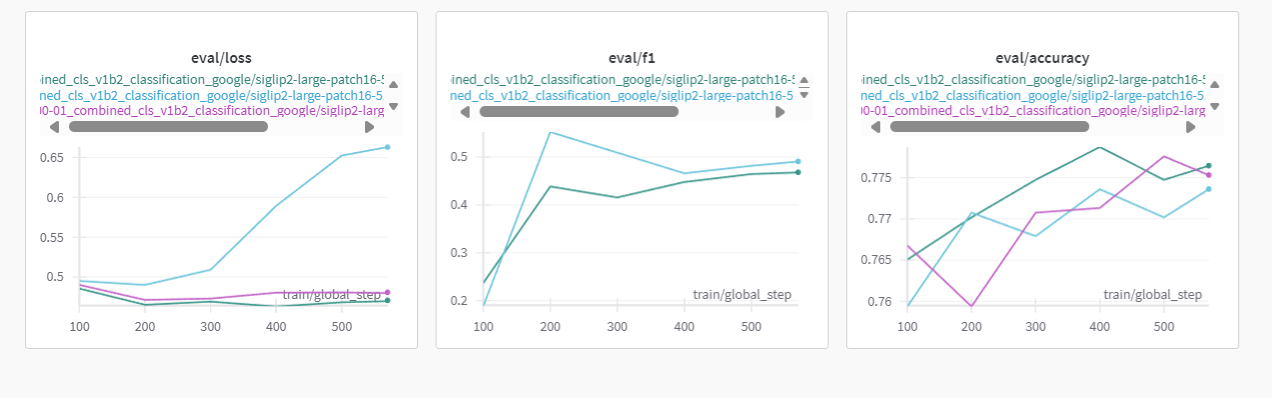
Clip Models:
- seems to perform better on bianry (AI throw / keep) than just the dino v2 large models.
on a 8xh100 machine, with training args:
- bs = 24x8; total 11k samples * 10e* = ~500 steps
#!/bin/bash
# Define variables
BASE_MODEL="google/siglip2-base-patch16-512"
DATASET="distill-lab/COMBINE_nai-distill_00-01_eagle.library"
TASK="classification"
NUM_EPOCHS=10
# Run training command
python -m trainlib.hf_trainer.cli \
--model_name_or_path $BASE_MODEL \
--dataset_name $DATASET \
--output_dir distill-n4_00-01_combined_cls_v1b2_classification_$BASE_MODEL \
--remove_unused_columns False \
--label_column_name star \
--task $TASK \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--eval_strategy steps \
--eval_steps 100 \
--learning_rate 5e-6 \
--num_train_epochs $NUM_EPOCHS \
--per_device_train_batch_size 24 \
--per_device_eval_batch_size 24 \
--logging_strategy steps \
--logging_steps 2 \
--save_total_limit 1 \
--seed 1337 \
--lr_scheduler_type cosine \
--dataloader_num_workers 16 \
--ignore_mismatched_sizes True
model = google/siglip2-base-patch16-512:
- (376M params)
wandb: Run summary:
wandb: eval/accuracy 0.76684
wandb: eval/loss 0.49165
wandb: eval/runtime 13.1276
wandb: eval/samples_per_second 134.602
wandb: eval/steps_per_second 0.762
wandb: total_flos 4.381485869237797e+19
wandb: train/epoch 10.0
wandb: train/global_step 530
wandb: train/grad_norm 16.72753
wandb: train/learning_rate 0.0
wandb: train/loss 0.3167
wandb: train_loss 0.43538
wandb: train_runtime 508.2728
wandb: train_samples_per_second 197.001
wandb: train_steps_per_second 1.043
model =google/siglip2-large-patch16-512:
train_transforms = Compose([
RandomResizedCrop(size),
RandomHorizontalFlip(),
ToTensor(),
normalize,
])- (882M params)
- twice the size, 1% increase in accuracy
wandb: Run summary:
wandb: eval/accuracy 0.77533
wandb: eval/loss 0.4809
wandb: eval/runtime 15.9025
wandb: eval/samples_per_second 111.114
wandb: eval/steps_per_second 0.692
wandb: total_flos 1.4915777670524436e+20
wandb: train/epoch 10.0
wandb: train/global_step 570
wandb: train/grad_norm 375217.9375
wandb: train/learning_rate 0.0
wandb: train/loss 0.286
wandb: train_loss 0.40591
wandb: train_runtime 1032.5423
wandb: train_samples_per_second 96.974
wandb: train_steps_per_second 0.552
modified augmentations:
train_transforms = Compose([
RandomResizedCrop(size=size, scale=(0.8, 1.0), ratio=(0.9, 1.1)),
RandomRotation(5),
RandomHorizontalFlip(p=0.2),
ColorJitter(brightness=0.1, contrast=0.1, saturation=0.1, hue=0.05),
RandomApply([GaussianBlur(kernel_size=3, sigma=(0.5, 1.5))], p=0.1),
ToTensor(),
normalize,
])- (reduce random crop, more light things like rotate / jitter)
- eval loss goes really high (and train loss goes down much faster)
- training with more subtle augmentations overfits?
ndb: eval/accuracy 0.77363
wandb: eval/f1 0.49109
wandb: eval/loss 0.66314
wandb: eval/precision 0.5452
wandb: eval/recall 0.44676
wandb: eval/roc_auc 0.77921
wandb: eval/runtime 17.0701
wandb: eval/samples_per_second 103.514
wandb: eval/steps_per_second 0.644
wandb: total_flos 1.4915777670524436e+20
wandb: train/epoch 10.0
wandb: train/global_step 570
wandb: train/grad_norm 524651.125
wandb: train/learning_rate 0.0
wandb: train/loss 0.0637
wandb: train_loss 0.26663
wandb: train_runtime 1073.7748
wandb: train_samples_per_second 93.25
wandb: train_steps_per_second 0.531modified augmentation 2 (heavier):
train_transforms = Compose([
# RandomResizedCrop(size=size, scale=(0.8, 1.0), ratio=(0.9, 1.1)),
RandomResizedCrop(size),
RandomRotation(5),
# RandomHorizontalFlip(p=0.2),
RandomHorizontalFlip(),
ColorJitter(brightness=0.1, contrast=0.1, saturation=0.1, hue=0.05),
RandomApply([GaussianBlur(kernel_size=3, sigma=(0.5, 1.5))], p=0.1),
ToTensor(),
normalize,
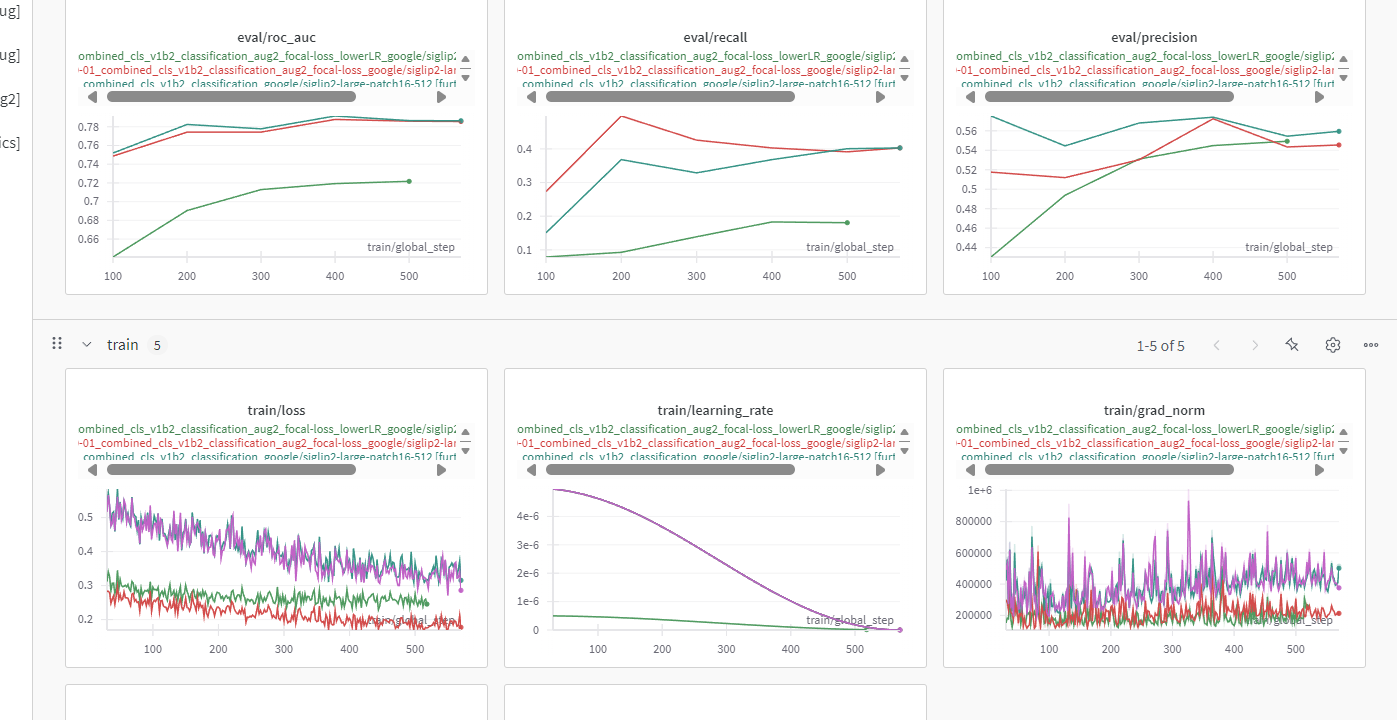
])- on binary classification of AI image filtering, accuracy (and other metrics) seems to benefit from heavy augmentations:
-
purple: original augments (crop/flip)
-
blue: augments1 (less crop/fip, slight jitter/rotate/blur)
-
green: aguments2 (original crop/flip + slight jitter/rotate/blur)
-
augment too little: overfits (eval loss goes up)
-
augment moderately: works (eval loss not going too up)
wandb: Run summary:
wandb: eval/accuracy 0.77646
wandb: eval/f1 0.46837
wandb: eval/loss 0.4708
wandb: eval/precision 0.55949
wandb: eval/recall 0.40278
wandb: eval/roc_auc 0.7864
wandb: eval/runtime 17.4719
wandb: eval/samples_per_second 101.134
wandb: eval/steps_per_second 0.63
wandb: total_flos 1.4915777670524436e+20
wandb: train/epoch 10.0
wandb: train/global_step 570
wandb: train/grad_norm 515768.625
wandb: train/learning_rate 0.0
wandb: train/loss 0.3154
wandb: train_loss 0.41385
wandb: train_runtime 1075.1719
wandb: train_samples_per_second 93.129
wandb: train_steps_per_second 0.53
modified augmentation 3 (even heavier):

train_transforms_aug3 = Compose([
T.RandomResizedCrop(size=size, scale=(0.5, 1.0), ratio=(0.75, 1.33)),
T.RandomRotation(5),
T.RandomHorizontalFlip(p=0.5),
T.RandomVerticalFlip(p=0.15), # Optional, depending on your task
T.ColorJitter(brightness=0.15, contrast=0.15, saturation=0.15, hue=0.05),
T.RandomApply([T.GaussianBlur(kernel_size=3, sigma=(0.5, 2.0))], p=0.3),
T.RandomPerspective(distortion_scale=0.3, p=0.5),
T.RandomAffine(degrees=2, translate=(0.1, 0.1), scale=(0.95, 1.05), shear=5),
T.ToTensor(),
normalize,
T.RandomErasing(p=0.5, scale=(0.02, 0.03), ratio=(0.3, 3.3)),
])
- worse result than aug2 (more subtle)
- accuracy went down; loss went up
wandb: Run summary:
wandb: eval/accuracy 0.76853
wandb: eval/f1 0.45101
wandb: eval/loss 0.50415
wandb: eval/precision 0.53674
wandb: eval/recall 0.38889
wandb: eval/roc_auc 0.77035
wandb: eval/runtime 17.9685
wandb: eval/samples_per_second 98.339
wandb: eval/steps_per_second 0.612
wandb: total_flos 1.4915777670524436e+20
wandb: train/epoch 10.0
wandb: train/global_step 570
wandb: train/grad_norm 494826.5
wandb: train/learning_rate 0.0
wandb: train/loss 0.2347
wandb: train_loss 0.37664
wandb: train_runtime 1082.901
wandb: train_samples_per_second 92.465
wandb: train_steps_per_second 0.526
modified augmentation 4 (tweak back a bit):
slightly reduced the ranges for aug3 and see if it improves accuracy (so we know if it’s too much of magnitude vs. one of transforms is fundamentally NOT good):

train_transforms_aug4 = Compose([
# Geometric transforms
T.RandomResizedCrop(size=size, scale=(0.8, 1.0), ratio=(0.75, 1.33)),
T.RandomRotation(15),
T.RandomHorizontalFlip(p=0.5),
T.RandomVerticalFlip(p=0.15),
T.RandomPerspective(distortion_scale=0.1, p=0.5), # Reduced from 0.3 for subtlety
T.RandomAffine(degrees=2, translate=(0.1, 0.1), scale=(0.98, 1.02), shear=3),
# Color and quality transforms
T.ColorJitter(brightness=0.15, contrast=0.15, saturation=0.15, hue=0.05), # Kept conservative
T.RandomApply([T.GaussianBlur(kernel_size=3, sigma=(0.5, 2.0))], p=0.3),
T.RandomAdjustSharpness(sharpness_factor=1.5, p=0.3), # New: subtle sharpness adjustment
# Conversion to tensor
T.ToTensor(),
# Post-tensor transforms
T.Lambda(lambda x: x + torch.randn_like(x) * 0.01), # New: slight Gaussian noise
normalize,
T.RandomErasing(p=0.5, scale=(0.01, 0.02), ratio=(0.3, 3.3)), # Adjusted scale slightly up
# T.RandomErasing(p=0.2, scale=(0.1, 0.2), ratio=(0.3, 3.3)), # New: occasional larger erasure
])Using Focal Loss:
# Run training command
python -m trainlib.hf_trainer.cli \
--model_name_or_path $BASE_MODEL \
--dataset_name $DATASET \
--output_dir distill-n4_00-01_combined_cls_v1b2_classification_aug2_focal-loss_$BASE_MODEL \
--remove_unused_columns False \
--label_column_name star \
--task $TASK \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--eval_strategy steps \
--eval_steps 100 \
--learning_rate 5e-6 \
--num_train_epochs $NUM_EPOCHS \
--per_device_train_batch_size 22 \
--per_device_eval_batch_size 22 \
--logging_strategy steps \
--logging_steps 2 \
--save_total_limit 1 \
--seed 1337 \
--lr_scheduler_type cosine \
--dataloader_num_workers 16 \
--ignore_mismatched_sizes True \
--fp16 True # EXTRA ARGUMENT
(siglip2 large, augment2, focal loss): similar performance with regular
wandb: Run summary:
wandb: eval/accuracy 0.77193
wandb: eval/f1 0.46338
wandb: eval/loss 0.24877
wandb: eval/precision 0.54545
wandb: eval/recall 0.40278
wandb: eval/roc_auc 0.78564
wandb: eval/runtime 17.8045
wandb: eval/samples_per_second 99.245
wandb: eval/steps_per_second 0.618
wandb: total_flos 1.4915777670524436e+20
wandb: train/epoch 10.0
wandb: train/global_step 570
wandb: train/grad_norm 212554.17188
wandb: train/learning_rate 0.0
wandb: train/loss 0.1774
wandb: train_loss 0.22022
wandb: train_runtime 1070.7678
wandb: train_samples_per_second 93.512
wandb: train_steps_per_second 0.532
wandb:
Using lower LR:
NEW: lower learning rate by 10 times and see what happens since this one suggest 1e-7 / 1e-8: https://github.com/openai/CLIP/issues/150
python -m trainlib.hf_trainer.cli \
--model_name_or_path $BASE_MODEL \
--dataset_name $DATASET \
--output_dir distill-n4_00-01_combined_cls_v1b2_classification_aug2_focal-loss_lowerLR_$BASE_MODEL \
--remove_unused_columns False \
--label_column_name star \
--task $TASK \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--eval_strategy steps \
--eval_steps 100 \
--learning_rate 5e-7 \
--num_train_epochs $NUM_EPOCHS \
--per_device_train_batch_size 22 \
--per_device_eval_batch_size 22 \
--logging_strategy steps \
--logging_steps 2 \
--save_total_limit 1 \
--seed 1337 \
--lr_scheduler_type cosine \
--dataloader_num_workers 16 \
--ignore_mismatched_sizes True \
--fp16 True # EXTRA ARGUMENTmetrics is more stable now (green curve):
Using Lower LR, Longer:
(5e-7 30e; mediocure results, no better than just using 5e-6 10e)

wandb: Run summary:
wandb: eval/accuracy 0.7691
wandb: eval/f1 0.4104
wandb: eval/loss 0.2466
wandb: eval/precision 0.54615
wandb: eval/recall 0.3287
wandb: eval/roc_auc 0.76975
wandb: eval/runtime 17.5273
wandb: eval/samples_per_second 100.814
wandb: eval/steps_per_second 0.628
wandb: total_flos 4.474733301157331e+20
wandb: train/epoch 30.0
wandb: train/global_step 1710
wandb: train/grad_norm 352201.21875
wandb: train/learning_rate 0.0
wandb: train/loss 0.2293
wandb: train_loss 0.24453
wandb: train_runtime 3093.8595
wandb: train_samples_per_second 97.092
wandb: train_steps_per_second 0.553
Using siglip2 giant:
actually had lower accuracy than say large, and overfits more easily. could be fluctuate but maybe not
wandb: Run summary:
wandb: eval/accuracy 0.75891
wandb: eval/f1 0.45524
wandb: eval/loss 0.56475
wandb: eval/precision 0.50857
wandb: eval/recall 0.41204
wandb: eval/roc_auc 0.77055
wandb: eval/runtime 19.4088
wandb: eval/samples_per_second 91.041
wandb: eval/steps_per_second 0.721
wandb: total_flos 3.090267103867837e+20
wandb: train/epoch 10.0
wandb: train/global_step 790
wandb: train/grad_norm 1113629.75
wandb: train/learning_rate 0.0
wandb: train/loss 0.2394
wandb: train_loss 0.35256
wandb: train_runtime 1717.9909
wandb: train_samples_per_second 58.283
wandb: train_steps_per_second 0.46
Random things to paste
Here’s a very heavy augmentation that kind of looks cool:
train_transforms = Compose([
# T.RandomResizedCrop(size=size, scale=(0.85, 1.0), ratio=(0.95, 1.05)),
T.RandomResizedCrop(size),
T.RandomRotation(5, fill=255),
T.RandomHorizontalFlip(p=0.5),
T.ColorJitter(brightness=0.1, contrast=0.1, saturation=0.1, hue=0.05),
T.ColorJitter(brightness=0.1, contrast=0.1, saturation=0.1, hue=0.05),
T.RandomApply([T.GaussianBlur(kernel_size=3, sigma=(0.5, 0.8))], p=0.05),
T.RandomAffine(degrees=0, translate=(0.03, 0.03), scale=(0.97, 1.03), fill=255),
T.ToTensor(),
normalize,
])

AES-iter3-min3:
gettin glabels from the argilla rating, choose images with lt least 3 rates, and train model on their average:
run2: (1st run had very bad params)
# =================== BEGIN NOTES =======================
# 1. forgot to turn warmup down from the previous train; but rmse seems good somehow (so very low lr helped)?
# also forgot to turn lr down.
# next run:
# lower lr; proper warmup
# =================== END NOTES ==========================
python train_localpath_e05.py \
--model_name_or_path "google/siglip2-large-patch16-512" \
--output_dir test_train_rating_min3_run2 \
--remove_unused_columns False \
--image_column_name "local_path" \
--label_column_name "aes_mean_score" \
--task regression \
--do_train True \
--do_eval True \
--learning_rate 1e-5 \
--num_train_epochs 20 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 22 \
--per_device_eval_batch_size 22 \
--logging_strategy steps \
--logging_steps 10 \
--eval_strategy steps \
--eval_steps 100 \
--save_strategy steps \
--save_steps 100 \
--seed 1337 \
--allow_no_dataset_arg True \
--dataloader_num_workers 16 \
--fp16 True \
--parquet_path "hf://datatmp/aesthetic-iter3-labelling-samples-min_3_rated_local_path" \
--ignore_mismatched_sizes True \
--warmup_steps 1000 \
--max_grad_norm 1.0 \
--lr_scheduler_type cosinewandb: Run summary:
wandb: eval/loss 0.55636
wandb: eval/mse 0.55711
wandb: eval/rmse 0.7464
wandb: eval/runtime 12.7365
wandb: eval/samples_per_second 32.427
wandb: eval/steps_per_second 0.236
wandb: total_flos 6.9595812462801715e+19
wandb: train/epoch 20.0
wandb: train/global_step 280
wandb: train/grad_norm 1618059.375
wandb: train/learning_rate 0.0
wandb: train/loss 0.3619
wandb: train_loss 2.0436
wandb: train_runtime 709.7309
wandb: train_samples_per_second 65.828
wandb: train_steps_per_second 0.395
run3: